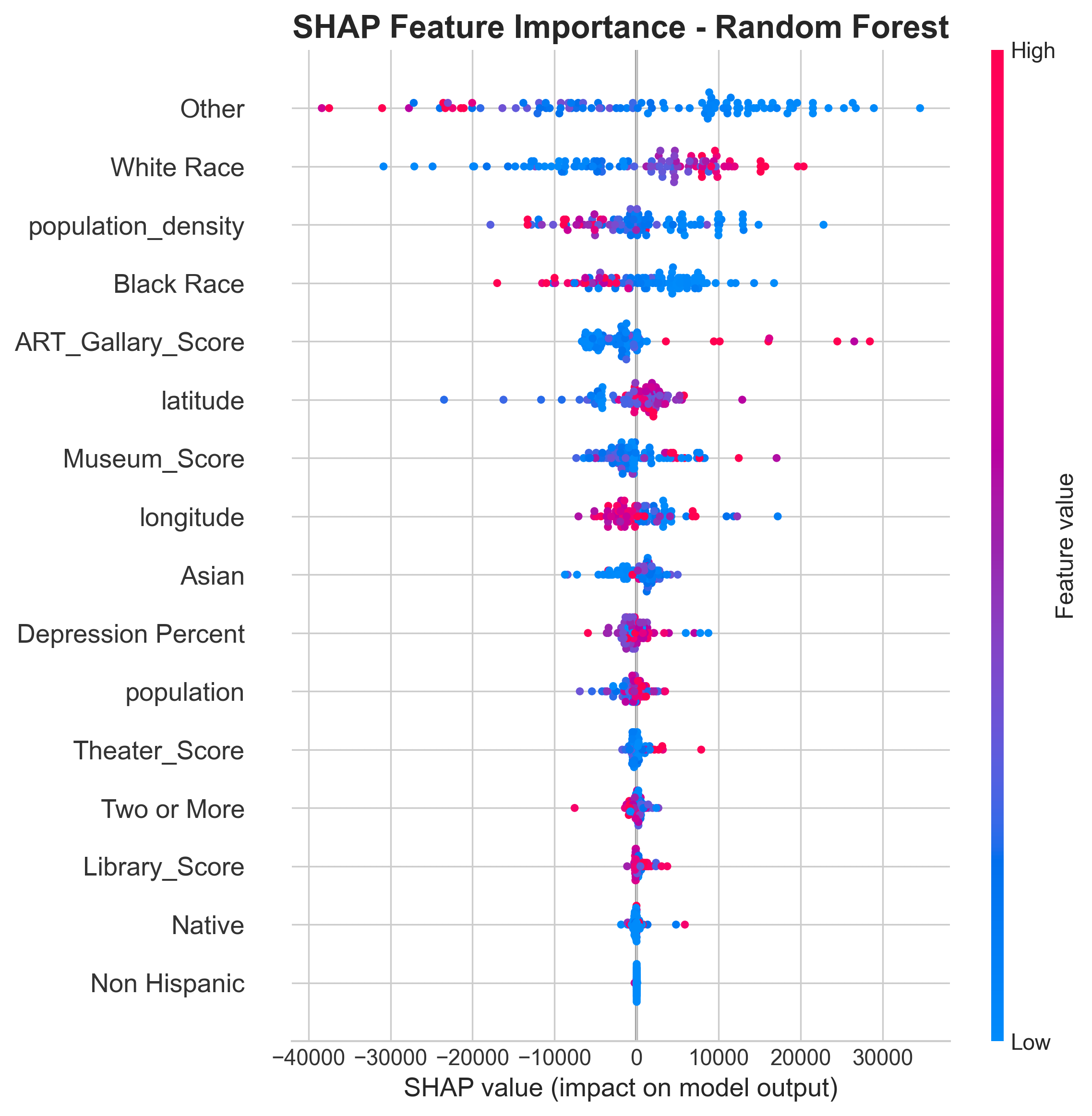
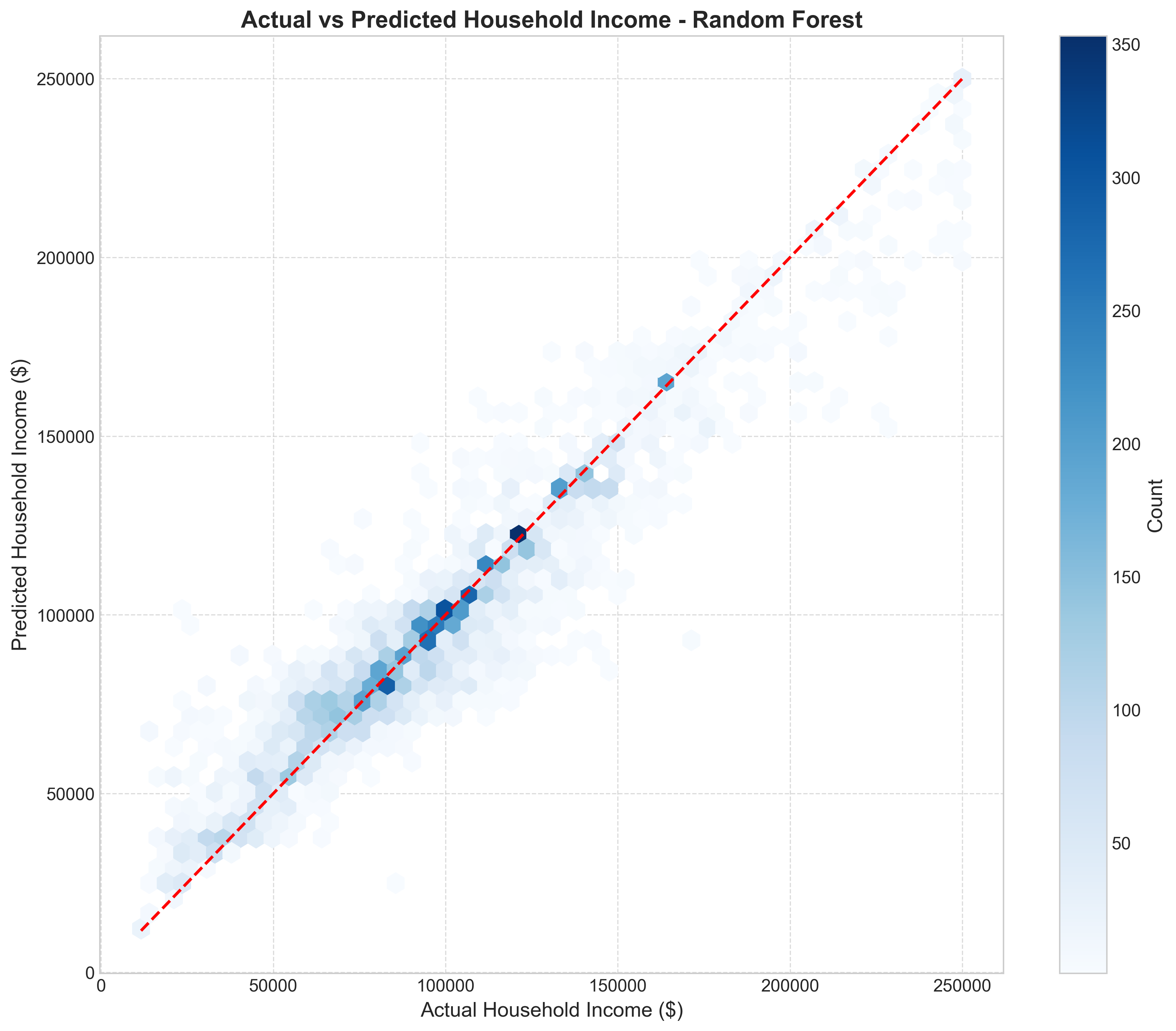
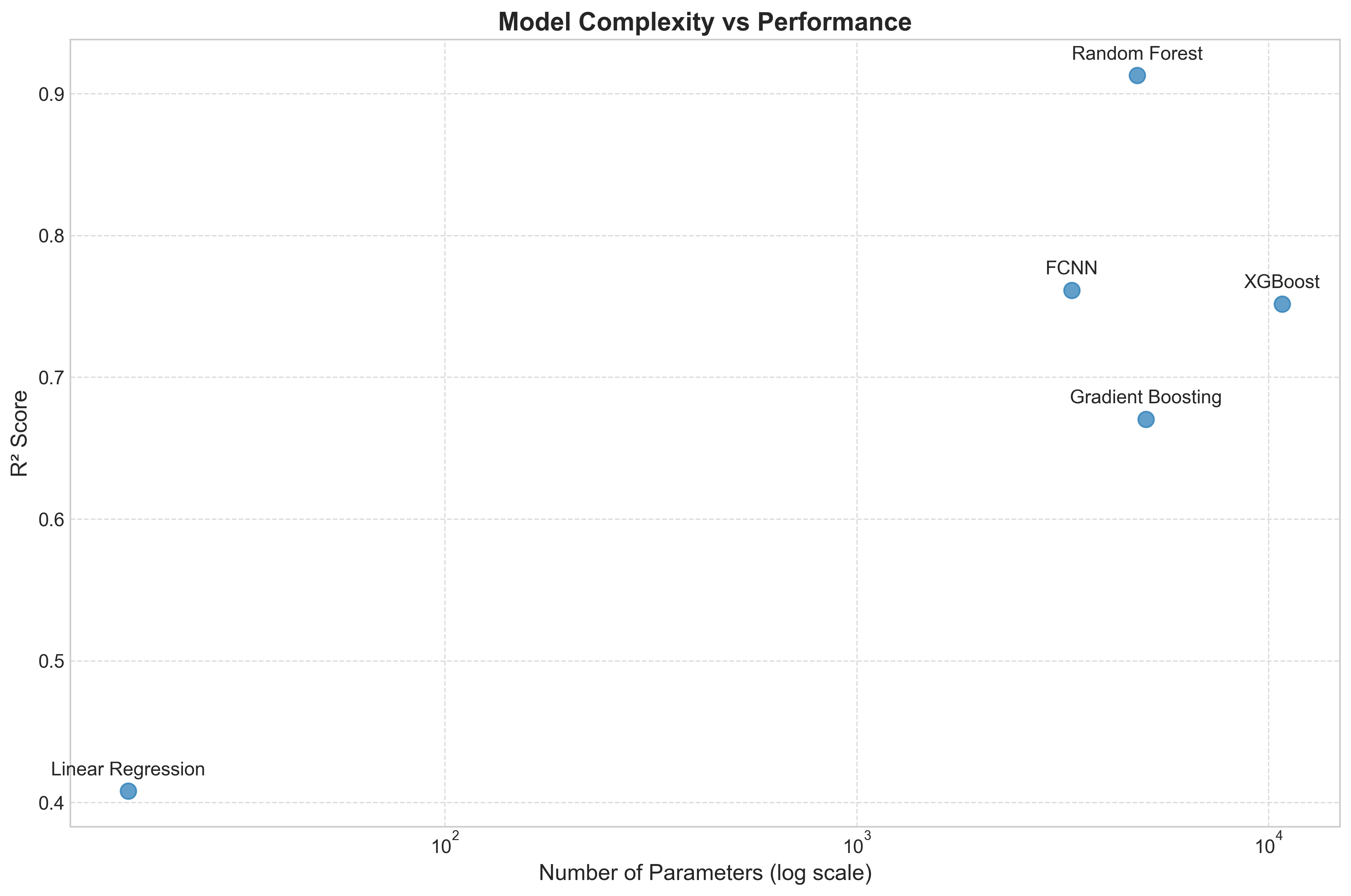
Dataset Preparation Methodology
Our research leverages a comprehensive dataset combining cultural infrastructure, geographic coordinates, and demographic variables to predict household income across New York City. Below we outline our data collection and processing methodology.
Explore the GeoSpatial Data in DetailsGeographic Grid Creation
We implemented a sophisticated spatial sampling approach using a 500x500 grid system spanning the geographic bounds of NYC. This high-resolution grid enables detailed spatial analysis and captures local variations in both cultural and demographic characteristics.
Cultural Score Computation
We developed an innovative approach to quantify cultural accessibility using an exponential decay function. This formula incorporates distance-based influence where cultural site weights diminish with distance from grid points.
Demographic Integration
Demographic features were integrated using U.S. Census data, including population density, racial composition statistics, and socioeconomic indicators. Spatial joins matched grid points with census polygons.
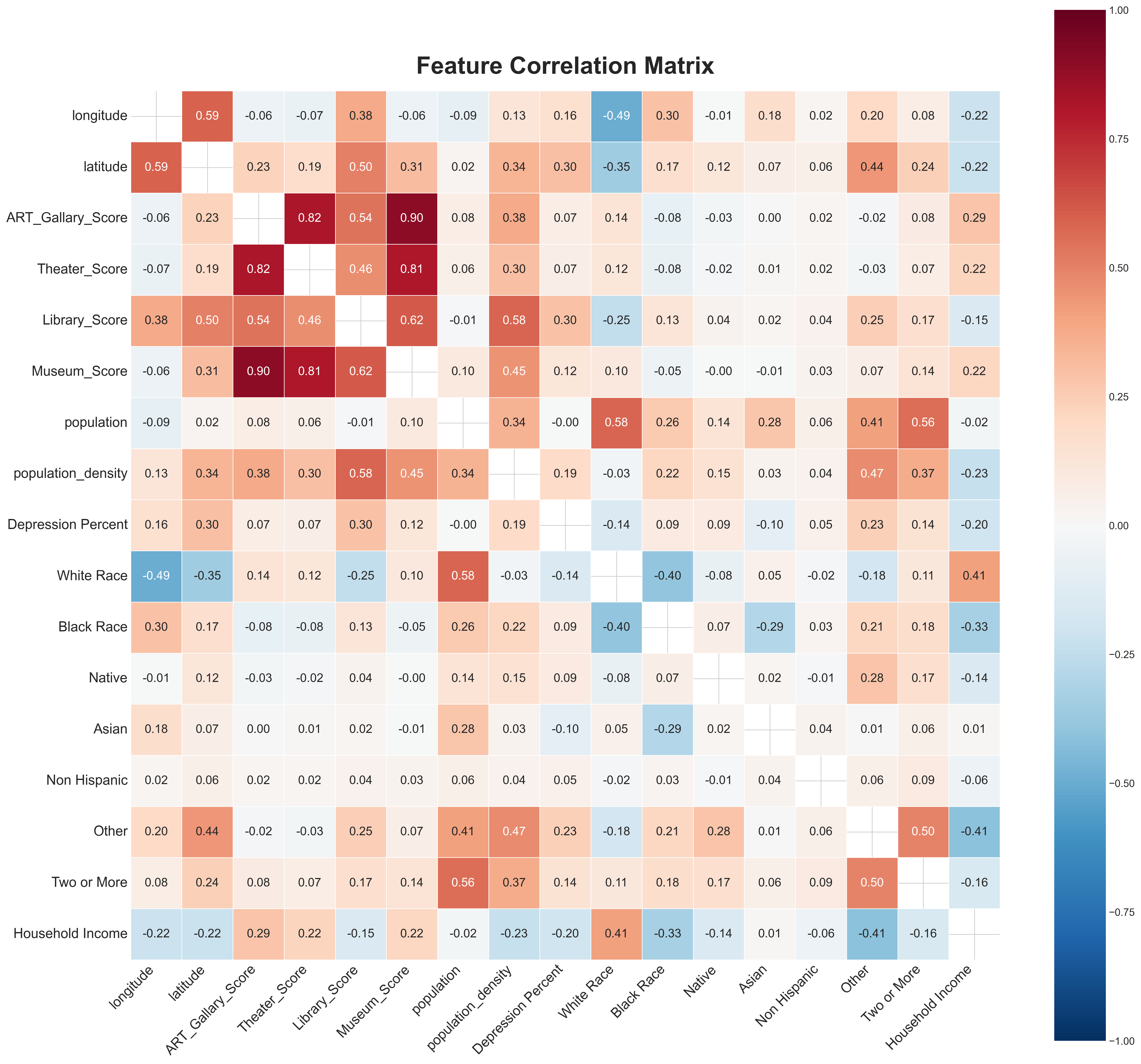
Feature correlation matrix highlighting relationships between variables in the dataset.
Final Dataset Description
- Features: Longitude, latitude, cultural scores, demographic variables
- Target: Household income ($)
- Total samples: 74,484 (after filtering for NYC boundaries)
- Grid resolution: 500x500